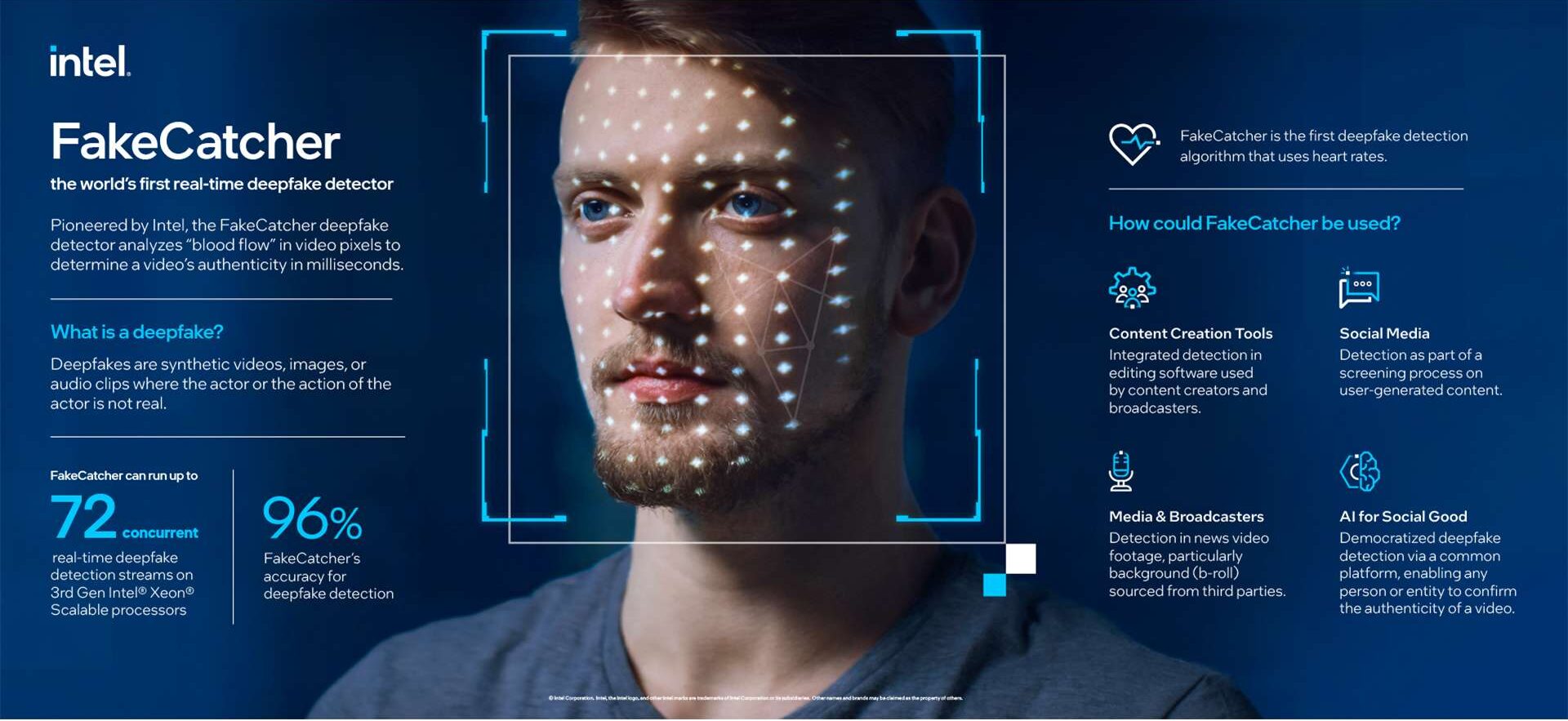
American technology company Intel on November 14 unveiled the FakeCatcher, its deepfake detection platform. The company said it is the world’s first real-time deepfake detector, which can detect fake videos in milliseconds with a 96 per cent accuracy rate. Here is everything you need to know about the Intel’s real-time deepfake detector tech FakeCatcher.
What is Deepfake:
Deepfake is essentially a video in which a person’s face or body has been digitally altered so that they appear to be someone else. Deception due to deepfakes can cause harm and mislead people, resulting in negative consequences like diminished trust in the media. It’s tough to detect these deepfake videos in real time as the detection apps take a lot of time for uploading videos for analysis, then hours for results.
How it Works:
Intel’s real-time platform uses FakeCatcher, a detector designed by Demir in collaboration with Umur Ciftci from the State University of New York at Binghamton. Using Intel hardware and software, it runs on a server and interfaces through a web-based platform. On the software side, a collection of specialist tools form the optimised FakeCatcher architecture, which the real-time platform uses to detect deepfake. On the hardware side, the real-time detection platform can run up to 72 different detection streams simultaneously on 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors.
Most of the deep learning-based detectors, which look at raw data to try to find signs of inauthenticity and identify what is wrong with a video. FakeCatcher looks for authentic clues in real videos. It assesses what makes us human – subtle blood flow in the pixels of a video. These blood flow signals are collected from all over the face and algorithms translate these signals into spatiotemporal maps. Then, using deep learning, it can instantly detect whether a video is real or fake.
Why it matters:
FakeCatcher helps restore trust by enabling users to distinguish between real and fake content. Intel suggests that there are several potential uses of FakeCatcher. Social media platforms can leverage the technology to prevent users from uploading harmful deepfake videos. Global news organizations can use the detector to avoid accidentally spreading manipulated videos. And, nonprofit organisations can employ the platform to democratize detection of deepfakes for everyone.